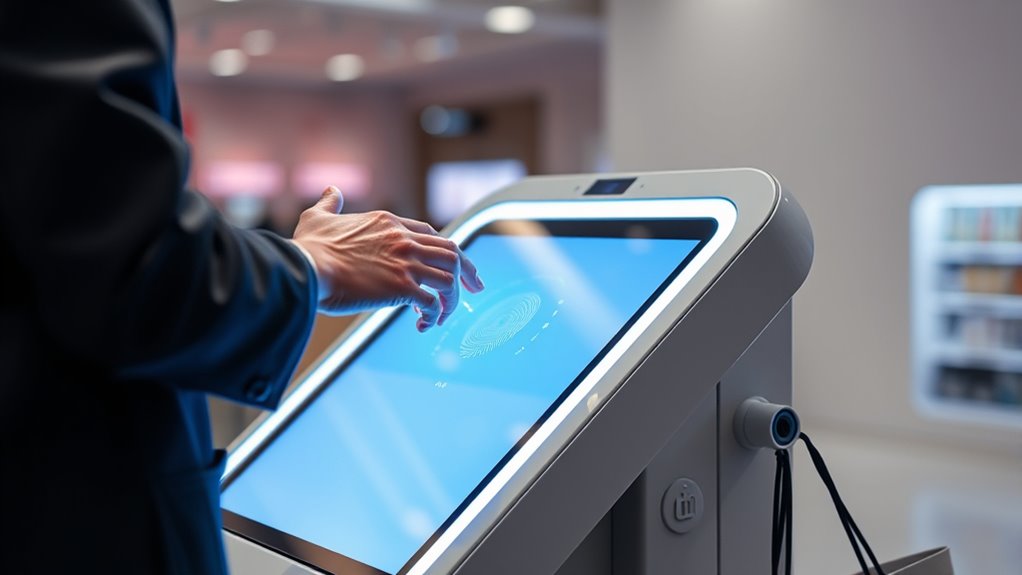
Biometric checkouts using fingerprints and Face ID are quickly becoming the new way to pay, offering faster, contactless, and more secure transactions. They streamline your shopping experience by reducing wait times and eliminating the need for cash or cards. Thanks to advancements in technology, these systems are more accurate and reliable than ever, with many stores investing in them. However, concerns about privacy and data security remain. If you keep exploring, you’ll discover how these innovations are shaping your shopping future.
Key Takeaways
- Biometric checkouts use fingerprint and face recognition to streamline payments, reducing wait times and enhancing shopping convenience.
- Advances in technology have made biometric systems more accurate and reliable, ensuring quick and seamless user identification.
- Privacy concerns arise over the storage and security of sensitive biometric data, prompting regulations like GDPR for protection.
- Retailers aim to improve customer experience and reduce theft with biometric solutions, promoting wider adoption.
- Ethical issues include data security, potential surveillance, and consumer rights, requiring careful balancing of innovation and privacy.
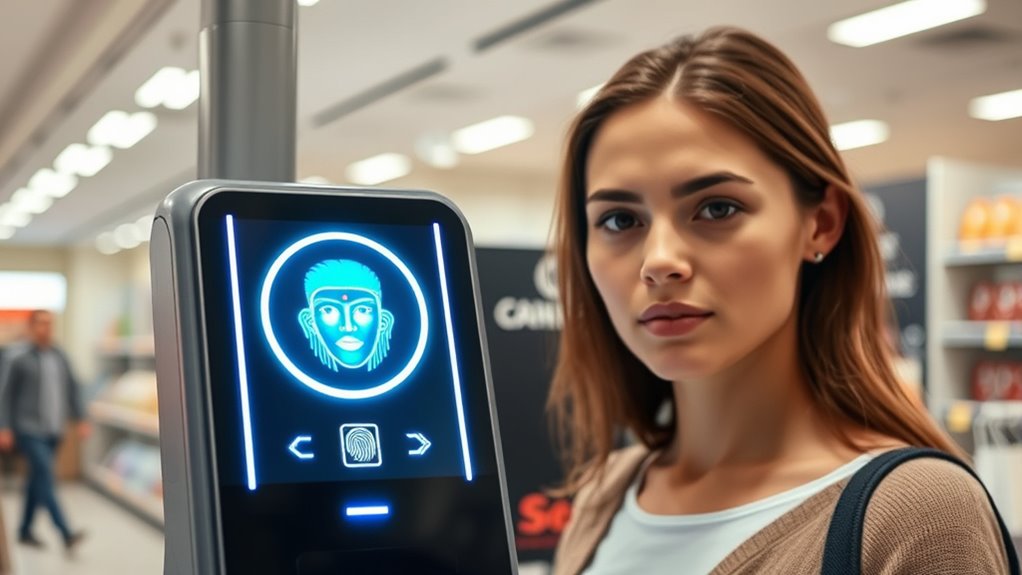

Biometric checkouts are transforming the way we shop by streamlining the payment process and reducing wait times. Instead of fumbling for cash or cards, you can simply use your fingerprint or face scan to complete your purchase quickly and efficiently. This shift towards biometric technology is driven by ongoing technological advancements that make these systems more accurate, faster, and easier to use. Retailers and tech companies are investing heavily in biometric solutions because they promise a seamless shopping experience. However, as you adopt these innovations, you might wonder about privacy concerns. Your biometric data is highly personal, and storing it raises questions about security and potential misuse. While many systems use encrypted storage and local authentication to protect your information, vulnerabilities still exist. Cybercriminals are continually finding ways to compromise systems, which fuels apprehension about how your biometric data is handled and whether it could be stolen or shared without your consent. Additionally, the integration of these systems with broader AI security measures highlights the importance of safeguarding sensitive information against emerging threats. These technological advancements have made biometric checkouts increasingly reliable and user-friendly. Modern fingerprint scanners and facial recognition software can identify you in seconds, even in crowded environments. The accuracy of these systems has improved dramatically thanks to machine learning algorithms and sophisticated sensors. As a result, you no longer need to worry about false rejections or mistaken identity, which were common issues in earlier versions of biometric technology. Retailers see these improvements as a way to enhance customer experience, cut down on checkout times, and reduce theft. With biometric checkouts, you can avoid the hassle of digging through your wallet or purse, making your shopping faster and more convenient. Despite the benefits, privacy concerns remain a significant hurdle. You might worry about where your biometric data is stored and who has access to it. Unlike credit card information, biometric data isn’t easily changeable if compromised, which makes its security paramount. Regulations like GDPR and other privacy laws aim to protect consumers, but enforcement varies. Some people feel uncomfortable sharing their biometric data at all, fearing it could be used for surveillance or profiling. Retailers must balance technological progress with respecting your privacy rights, ensuring transparent policies and robust security measures. As biometric checkout systems become more widespread, you’ll need to stay informed about how your data is protected and what rights you have. This ongoing evolution of technology offers convenience but also demands vigilance to safeguard your personal information.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Secure Are Biometric Checkout Systems Against Hacking?
Biometric checkout systems are generally secure, but they’re not invulnerable to biometric hacking or security vulnerabilities. Hackers can attempt to spoof fingerprints or facial recognition, especially if systems aren’t well-protected. To stay safe, you should use strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regularly update software. While biometric data is harder to steal than cards, understanding potential risks helps you better protect your personal information during transactions.
What Are the Privacy Policies for Storing Biometric Data?
You might think your biometric data is safe, but privacy policies often prioritize convenience over security. They typically require biometric data encryption to protect your info, but the real catch is user consent protocols—you’re often giving permission without fully understanding how your data’s stored or shared. Be cautious; companies may keep your biometric info longer than you’d like, risking misuse or breaches despite claims of strict privacy safeguards.
Can Biometric Checkouts Be Used Anonymously?
Biometric checkouts generally can’t be used for completely anonymous transactions because your biometric data links directly to your identity. While some systems may offer biometric anonymity by masking or encrypting your data, most require you to register your fingerprint or Face ID, making it traceable. For true anonymous transactions, traditional methods like cash are still the best option, as biometric data inevitably ties back to your personal identity.
Are There Age Restrictions for Biometric Payment Methods?
You might be surprised that many countries set age restrictions for biometric payment methods, aiming to protect minors. Usually, user eligibility begins at age 13 or 16, depending on local laws. These restrictions make certain that children aren’t using biometric data unsupervised, safeguarding their privacy. So, yes, age restrictions apply, and they help regulate who can use biometric payment options, making the system safer for younger users.
How Do Biometric Systems Handle False Rejections or Errors?
You might experience false rejections or errors with biometric systems, but they’re designed to minimize these issues. They handle false rejection rates by using error mitigation strategies like multiple authentication attempts and fallback options such as PINs or passwords. These systems continuously improve accuracy through advanced algorithms and adaptive learning, ensuring smoother transactions and reducing frustration. If errors occur, alternative verification methods keep your checkout process seamless and secure.
Conclusion
As you step into the future of shopping, biometric checkouts promise speed and security, making cash or cards feel like dial-up internet. While it’s tempting to embrace this tech revolution, remember the lessons from the past—trust and privacy still matter. So, as you wave goodbye to cash, ask yourself: are you ready to trade your fingerprint for convenience, or will you hold onto old-school safeguards? The checkout counter may never be the same.